What is e-invoicing under GST?
‘e-Invoicing’ or ‘electronic invoicing’ is a system in which B2B invoices are authenticated electronically by GSTN for further use on the common GST portal. Under the electronic invoicing system, an identification number will be issued against every invoice by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), managed by the GST Network (GSTN). The National Informatics Centre launched the first IRP at einvoice1.gst.gov.in.
All invoice information will be transferred from this portal to both the GST portal and e-way bill portal in real-time. Therefore, it will eliminate the need for manual data entry while filing GSTR-1 returns and generation of part-A of the e-way bills, as the information is passed directly by the IRP to the GST portal.
To whom is e-invoicing applicable?
| Phase | Applicable to taxpayers having aggregate turnover of more than | Applicable date | Notification number |
| I | Rs 500 crore | 01.10.2020 | 61/2020 – Central Tax and 70/2020 – Central Tax |
| II | Rs 100 crore | 01.01.2021 | 88/2020 – Central Tax |
| III | Rs 50 crore | 01.04.2021 | 5/2021 – Central Tax |
| IV | Rs 20 crore | 01.04.2022 | 1/2022 – Central Tax |
The taxpayers must comply with e-invoicing if the turnover exceeds the specified limit in any financial year from 2017-18 to 2021-22. Also, the aggregate turnover will include the turnover of all GSTINs under a single PAN across India.
Suppose ABC ltd aggregate turnover was as follows:
FY 2017-18: Rs 15 crore
FY 2018-19: Rs 17 crore
FY 2019-20: Rs 24 crore
FY 2020-21: Rs 19 crore
FY 2021-22: Rs 18 crore (till date)
The ABC ltd shall mandatorily generate e-invoices from 01.04.2022 irrespective of current year aggregate turnover as it has crossed the Rs 20 crore turnover limit in FY 2019-20.
However, irrespective of the turnover, e-Invoicing shall not be applicable to the following categories of registered persons for now, as notified in CBIC Notification No.13/2020 – Central Tax:
- An insurer or a banking company or a financial institution, including an NBFC
- A Goods Transport Agency (GTA)
- A registered person supplying passenger transportation services
- A registered person supplying services by way of admission to the exhibition of cinematographic films in multiplex services
- An SEZ unit (excluded via CBIC Notification No. 61/2020 – Central Tax)
- A government department and Local authority (excluded via CBIC Notification No. 23/2021 – Central Tax)
What is the current system in place for issuing invoices?
Currently, businesses generate invoices through various software, and the details of these invoices are manually uploaded in the GSTR-1 return. Once the respective suppliers file the GSTR-1, the invoice information is reflected in GSTR-2A for the recipients for viewing only. On the other hand, the consignor or transporters must generate e-way bills by again importing the invoices in excel or JSON manually.
Under the e-invoicing system (to be implemented from 1st October 2020), the process of generating and uploading invoice details will remain the same. It will be done by importing using the excel tool/JSON or via API integration, either directly or through a GST Suvidha Provider (GSP). The data will seamlessly flow to GSTR-1 preparation and for the e-way bill generation too. The e-invoicing system will be the key tool to enable this.
What is the process of getting an e-invoice?
The following are the stages involved in generating or raising an e-invoice.
- The taxpayer has to ensure to use the reconfigured ERP system as per PEPPOL standards. He could coordinate with the software service provider to incorporate the standard set for e-invoicing, i.e. e-invoice schema (standards) and must have the mandatory parameters notified by the CBIC, at least.
- Any taxpayer has got primarily two options for IRN generation:
- The IP address of the computer system can be whitelisted on the e-invoice portal for a direct API integration or integration via GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) such as ClearTax.
- Download the bulk generation tool to bulk upload invoices. It will generate a JSON file that can be uploaded on the e-invoice portal to generate IRNs in bulk.
- The taxpayer must thereafter raise a regular invoice on that software. He must give all the necessary details like billing name and address, GSTN of the supplier, transaction value, item rate, GST rate applicable, tax amount, etc.
- Once either of the above options is chosen, raise the invoice on the respective ERP software or billing software. Thereafter, upload the details of the invoice, especially mandatory fields, onto the IRP using the JSON file or via an application service provider (app or through GSP) or through direct API. The IRP will act as the central registrar for e-invoicing and its authentication. There are several other modes of interacting with IRP, such as SMS-based and mobile app-based.
- IRP will validate the key details of the B2B invoice, check for any duplications and generate an invoice reference number (hash) for reference. There are four parameters based on which IRN is generated: Seller GSTIN, invoice number, FY in YYYY-YY, and document type (INV/DN/CN).
- IRP generates the invoice reference number (IRN), digitally signs the invoice and creates a QR code in Output JSON for the supplier. On the other hand, the seller of the supply will get intimated of the e-invoice generation through email (if provided in the invoice).
- IRP will send the authenticated payload to the GST portal for GST returns. Additionally, details will be forwarded to the e-way bill portal, if applicable. The GSTR-1 of the seller gets auto-filled for the relevant tax period. In turn, it determines the tax liability.
A taxpayer can continue to print his invoice as being done presently with a logo. The e-invoicing system only mandates all taxpayers to report invoices on IRP in electronic format.
How will e-invoicing benefit businesses?
Businesses will have the following benefits by using e-invoice initiated by GSTN:
- e-Invoice resolves and plugs a major gap in data reconciliation under GST to reduce mismatch errors.
- e-Invoices created on one software can be read by another, allowing interoperability and help reduce data entry errors.
- Real-time tracking of invoices prepared by the supplier is enabled by e-invoice.
- Backward integration and automation of the tax return filing process – the relevant details of the invoices would be auto-populated in the various returns, especially for generating the part-A of e-way bills.
- Faster availability of genuine input tax credit.
- Lesser possibility of audits/surveys by the tax authorities since the information they require is available at a transaction level.
How will e-invoicing curb tax evasion?
It will help in curbing tax evasion in the following ways:
- Tax authorities will have access to transactions as they take place in real-time since the e-invoice will have to be compulsorily generated through the GST portal.
- There will be less scope for manipulating invoices since the invoice gets generated before carrying out a transaction.
- It will reduce the chances of fake GST invoices, and the only genuine input tax credit can be claimed as all invoices need to be generated through the GST portal. Since the input credit can be matched with output tax details, it becomes easier for GSTN to track fake tax credit claims.
What are the mandatory fields of an e-invoice?
e-Invoice must primarily adhere to the GST invoicing rules. Apart from this, it should also accommodate the invoicing system or policies followed by each industry or sector in India. Certain information is made mandatory, whereas the rest of it is optional for businesses. Many fields are also made optional, and users can choose to fill up relevant fields only. It has also described every field along with the sample inputs for the interested users. One can see that certain required fields from the e-way bill format are included now in the e-invoice, such as the sub supply type.
Below is the gist of the contents of the latest e-invoice format as notified on 30th July 2020 via Notification No.60/2020 – Central Tax:
- 12 sections (mandatory + optional) and six annexures consisting of a total of 138 fields.
- Out of the 12 sections, five are mandatory, and seven are optional. Two annexures are mandatory.
- The five mandatory sections are basic details, supplier information, recipient information, invoice item details, and document total. The two mandatory annexures are details of the items and the document total.
The following fields must be compulsorily be declared in an e-invoice:
| Sl. no. | Name of the field | List of choices/ specifications/sample Inputs | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Document Type Code | Enumerated List such as INV/CRN/DBN | Type of document must be specified |
| 2 | Supplier_Legal Name | String Max length: 100 | Legal name of the supplier must be as per the PAN card |
| 3 | Supplier_GSTIN | Max length: 15 Must be alphanumeric | GSTIN of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 4 | Supplier_Address | Max length: 100 | Building/Flat no., Road/Street, Locality, etc. of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 5 | Supplier_Place | Max length: 50 | Supplier’s location such as city/town/village must be mentioned |
| 6 | Supplier_State_Code | Enumerated list of states | The state must be selected from the latest list given by GSTN |
| 7 | Supplier Pincode | Six digit code | The place (locality/district/state) of the supplier’s locality |
| 8 | Document Number | Max length: 16 Sample can be “ Sa/1/2019” | For unique identification of the invoice, a sequential number is required within the business context, time frame, operating systems and records of the supplier. No identification scheme is to be used. |
| 9 | Preceeding_Invoice_Reference and date | Max length:16 Sample input is “ Sa/1/2019” and “16/11/2020” | Detail of original invoice which is being amended by a subsequent document such as a debit and credit note. It is required to keep future expansion of e-versions of credit notes, debit notes and other documents required under GST. |
| 10 | Document Date | String (DD/MM/YYYY) as per the technical field specification | The date when the invoice was issued. However, the format under explanatory notes refers to ‘YYYY-MM-DD’. Further clarity will be required. Document period start and end date must also be specified if selected. |
| 11 | Recipient_ Legal Name | Max length: 100 | The name of the buyer as per the PAN |
| 12 | Recipient’s GSTIN | Max length: 15 | The GSTIN of the buyer to be declared here |
| 13 | Recipient’s Address | Max length: 100 | Building/flat no., road/street, locality, etc. of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 14 | Recipient’s State Code | Enumerated list | The place of supply state code to be selected here |
| 15 | Place_Of_Supply_State_ Code | Enumerated list of states | The state must be selected from the latest list given by GSTN |
| 16 | Pincode | Six digit code | The place (locality/district/state) of the buyer on whom the invoice is raised/ billed to must be declared here if any |
| 17 | Recipient Place | Max length: 100 | Recipient’s location (City/Town/Village) |
| 18 | IRN- Invoice Reference Number | Max length: 64 Sample is ‘a5c12dca8 0e7433217…ba4013 750f2046f229’ | At the time of the registration request, this field is left empty by the supplier. Later on, a unique number will be generated by GSTN after uploading the e-invoice on the GSTN portal. An acknowledgement will be sent back to the supplier after the successful acceptance of the e-invoice by the portal. IRN should then be displayed on the e-invoice before use. |
| 19 | ShippingTo_GSTIN | Max length: 15 | GSTIN of the buyer himself or the person to whom the particular item is being delivered to |
| 20 | Shipping To_State, Pincode and State code | Max length: 100 for state, 6 digit pincode and enumerated list for code | State pertaining to the place to which the goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 21 | Dispatch From_ Name, Address, Place and Pincode | Max length: 100 each and 6 digit for pincode | Entity’s details (name, and city/town/village) from where goods are dispatched |
| 22 | Is_Service | String (Length: 1) by selecting Y/N | Whether or not supply of service must be mentioned |
| 23 | Supply Type Code | Enumerated list of codes Sample values can be either of B2B/B2C/ SEZWP/S EZWOP/E XP WP/EXP WOP/DE XP | Code will be used to identify types of supply such as business to business, business to consumer, supply to SEZ/exports with or without payment, and deemed export. |
| 24 | Item Description | Max length: 300 The sample value is ‘Mobile’ The schema document refers to this as the ‘identification scheme identifier of the Item classification identifier’ | Simply put, the relevant description is generally used for the item in the trade. However, more clarity is needed on how it needs to be described for every two or more items belonging to the same HSN code. |
| 25 | HSN Code | Max length: 8 | The applicable HSN code for particular goods/service must be entered |
| 26 | Item_Price | Decimal (12,3) Sample value is ‘50’ | The unit price, exclusive of GST, before subtracting item price discount, can not be negative |
| 27 | Assessable Value | Decimal (13,2) Sample value is ‘5000’ | The price of an item, exclusive of GST, after subtracting the item price discount. Hence, gross price (-) discount = net price item, if any cash discount is provided at the time of sale |
| 28 | GST Rate | Decimal (3,2) Sample value is ‘5’ | The GST rate represented as a percentage that is applicable to the item being invoiced |
| 29 | IGST Value, CGST Value and SGST Value Separately | Decimal (11,2) Sample value is ‘650.00’ | For each individual item, IGST, CGST and SGST amounts have to be specified |
| 30 | Total Invoice Value | Decimal (11,2) | The total amount of the Invoice with GST. Must be rounded to a maximum of 2 decimals |
How does the e-invoice look like?
The e-invoice format notified is as follows: 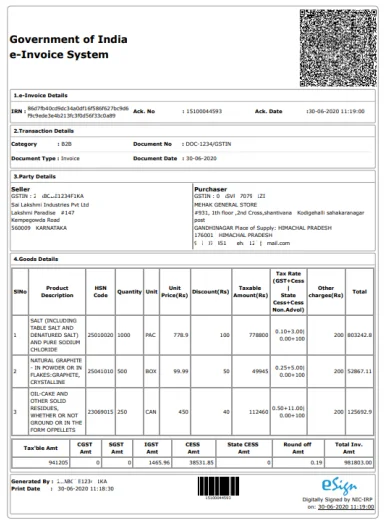
Check out detailed format of an e-invoice
FAQs on e-invoicing
To whom will e-invoicing apply
The e-invoicing system applies to the GST registered persons whose aggregate turnover in the financial year exceeds Rs.50 crore. From 1st April 2022, it shall apply to those with a turnover of more than Rs.20 crore. However, exceptions include Special Economic Zones (SEZ) units, insurance, banking, financial institutions, NBFCs, GTA, passenger transportation service, and sale of movie tickets. However, exceptions include Special Economic Zones (SEZ) units, insurance, banking, financial institutions, NBFCs, GTA, passenger transportation service, and sale of movie tickets.
Can an e-invoice be cancelled partially/fully?
An e-invoice cannot be cancelled partially but can be cancelled wholly. On cancellation, it must be reported to the IRN within 24 hours. Any attempt to cancel thereafter cannot be done on the IRN and must be manually cancelled on the GST portal before the returns are filed.
Will the bulk uploading of invoices for the generation of IRN be possible?
No, invoices must be uploaded one at a time into the IRP. The ERP of a business will need to be designed to place the request for the upload of individual invoices.
Will there be a facility for e-invoice generation on the common GST portal?
No, invoices will continue to be generated on the individual ERP software currently in use by businesses. The invoice must adhere to the e-invoicing standard format and include the mandatory parameters. The direct generation of invoices on a common portal is not being planned at the moment.
What are the types of documents that are to be reported into the IRP?
The documents that will be covered under the e-invoicing system are as follows-
- Invoices by the supplier
- Credit notes by the supplier
- Debit notes by the recipient
- Any other document as notified under GST law to be reported as an e-invoice by the creator of the document
For more FAQs on e-Invoicing, read our article on e-Invoicing FAQs.
